7 Cyber Security Myths Every Business Leader Should Stop Believing
- 1 min read
Discover 7 common cyber security myths that mislead business leaders and learn what actually reduces cyber risk in modern IT environments.

Introduction
Cyber threats are evolving faster than most organizations can adapt. Yet many executive decisions are still shaped by outdated cyber security myths that create blind spots and false confidence.
For business leaders, cyber security is no longer a purely technical topic. It is a board level risk and continuity issue that directly affects revenue, reputation, and regulatory exposure.
Teams across European enterprises, including those supported through Euro IT Sourcing delivery models, increasingly see that risk comes not from lack of tools, but from wrong assumptions. Let’s correct the most common ones.
Myth 1: We Are Too Small to Be a Target
Attackers do not only target large enterprises. Small and mid sized companies are often easier to breach.
Why smaller firms are attractive:
- Weaker security controls
- Lower monitoring maturity
- Fewer dedicated security staff
- Trusted supplier access to larger partners
According to EU cyber agency ENISA, supply chain and SME attacks are steadily increasing: https://www.enisa.europa.eu
Size does not reduce exposure. It often increases it.
Myth 2: Our Cloud Provider Handles All Security
Cloud platforms secure the infrastructure, not your configurations and data.
This is known as the shared responsibility model.
Cloud providers secure:
- Physical data centers
- Core platform infrastructure
- Base network controls
You are still responsible for:
- Identity and access management
- Data protection settings
- Application security
- Misconfiguration risks
NIST documents this shared model clearly in its cloud guidance: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov
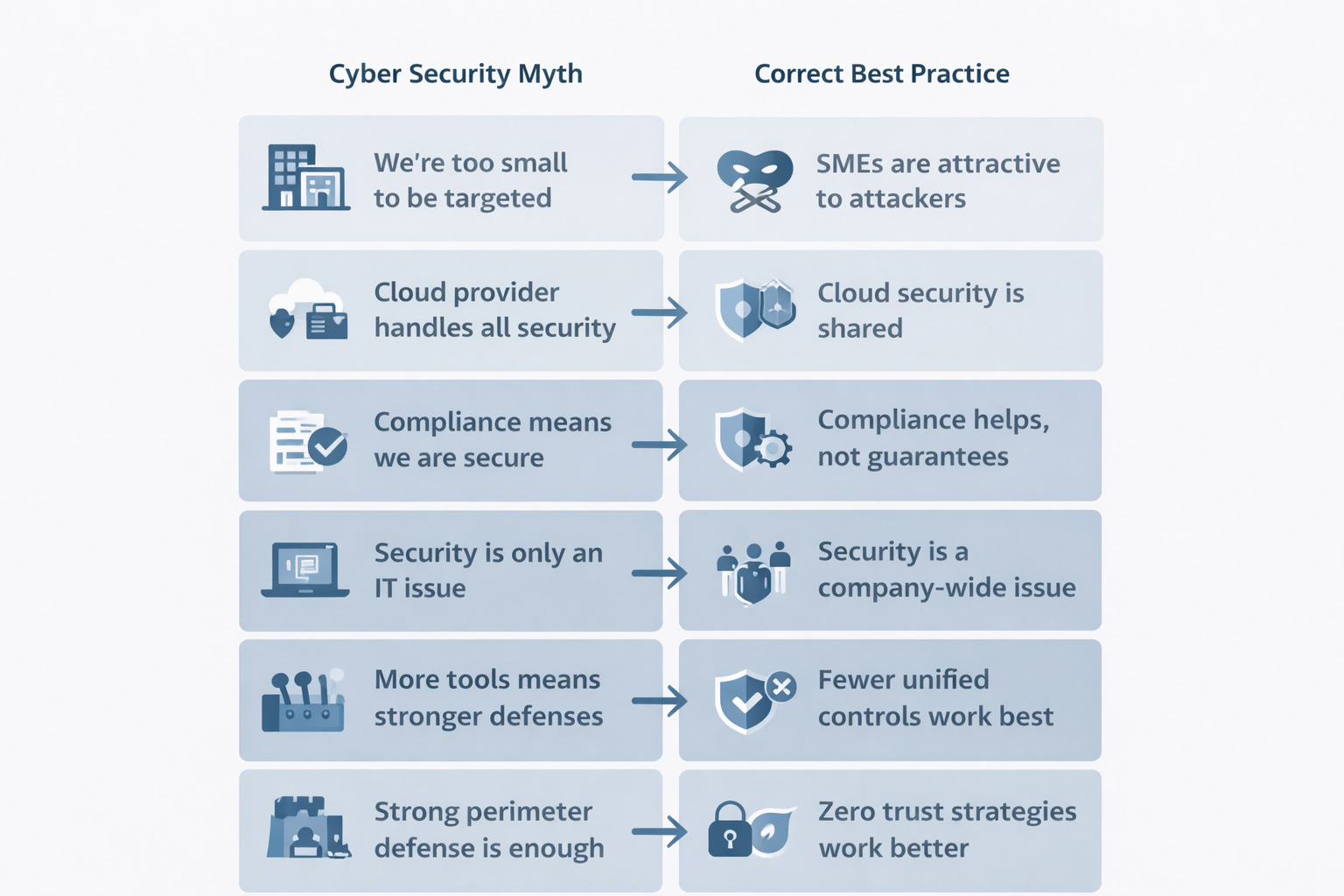
Myth 3: Compliance Means We Are Secure
Compliance is a minimum baseline, not proof of security maturity.
Common compliance gaps:
- Controls exist but are not continuously monitored
- Policies are documented but not enforced
- Audit scope is limited and periodic
- Real attack paths are not tested
Standards like ISO 27001 improve structure, but security posture requires continuous validation, not checklist completion: https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html
Myth 4: Cyber Security Is Only an IT Department Issue
Most successful attacks exploit people and processes, not only technology.
High impact breach vectors include:
- Phishing and social engineering
- Credential reuse
- Privilege misuse
- Vendor access channels
Cyber security must involve:
- Executive leadership
- HR and training teams
- Procurement and vendor management
- Legal and compliance functions
Security is an organizational discipline, not just an IT function.
Myth 5: More Tools Equal Better Security
Tool sprawl often reduces visibility and increases risk.
Common problems with too many tools:
- Alert overload
- Integration gaps
- Conflicting signals
- Unmanaged configurations
- Higher operational complexity
Modern security maturity focuses on:
- Control coverage
- Signal correlation
- Automation
- Response speed
Fewer well integrated controls outperform many disconnected ones.
Myth 6: Strong Perimeter Defense Is Enough
Perimeter based security models are outdated. Workloads and users now operate everywhere.
Drivers of perimeter collapse:
- Remote work
- SaaS adoption
- API integrations
- Partner connectivity
Modern models emphasize:
- Zero trust access
- Continuous verification
- Identity centric controls
- Least privilege enforcement
Zero trust architecture guidance is strongly promoted by NIST frameworks.
Myth 7: Cyber Security ROI Cannot Be Measured
Security value can be measured using risk and resilience metrics.
Measurable indicators include:
- Incident frequency trends
- Mean time to detect and respond
- Control coverage rates
- Vulnerability remediation speed
- Downtime reduction
Security ROI appears through:
- Lower breach probability
- Reduced incident impact
- Faster recovery
- Lower regulatory risk
Leading firms now treat cyber security as risk reduction investment, not pure cost.
Industry Insight
Global research from major consulting and analyst firms shows a consistent pattern:
- Most breaches trace back to identity and access weaknesses
- Misconfiguration is a top cloud breach driver
- Human factors remain the largest attack surface
- Detection speed matters more than prevention perfection
Market reports repeatedly show that cyber resilience maturity, not tool count, correlates with lower breach impact.
Euro IT Sourcing Perspective
From our experience working with European tech firms, cyber security failures are rarely caused by missing products. They are caused by misaligned assumptions and fragmented execution.
Patterns we frequently observe:
- Security controls not embedded into delivery pipelines
- Vendor access not continuously reviewed
- Rapid scaling without security architecture updates
- Dev and security teams operating in silos
Integrated delivery models with shared standards, secure engineering practices, and controlled access design significantly reduce operational risk.
Results and Impact
Organizations that move beyond cyber security myths typically achieve:
- Faster incident detection and containment
- Lower misconfiguration exposure
- Reduced third party risk
- Stronger audit outcomes
- Improved executive risk visibility
Typical benchmark improvements include:
- 30 to 50 percent faster remediation cycles
- Significant phishing success rate reduction after training programs
- Measurable drop in critical vulnerability backlog
Key Takeaways
- Company size does not reduce cyber risk
- Cloud security is shared, not outsourced completely
- Compliance is not equal to protection
- Security is a business wide responsibility
- Fewer integrated controls beat tool sprawl
Author and Contact
Author: Matt Borekci Contact Us: Euro IT Sourcing

What Does a Cyber Security Expert Do? A Complete Guide
Discover what a cyber security expert does, their roles, skills, and how they protect businesses from digital threats.

How Much Does a Cyber Security Expert Earn? Salary Insights for 2025
Explore 2025 cybersecurity salary trends, including global averages, roles in demand, and how outsourcing impacts IT security hiring.