How Cyber Security Experts Strengthen Remote Work Environments
- 1 min read
Discover how cyber security experts protect remote work environments by reducing risk, improving compliance, and strengthening digital resilience.

Introduction
Remote work has evolved from a temporary solution into a permanent operating model for many organizations. While it delivers flexibility and access to global talent, it also significantly expands the attack surface.
Distributed teams, personal devices, cloud collaboration tools, and home networks introduce new cyber security risks that traditional perimeter-based defenses were never designed to handle.
This is where experienced cyber security experts play a critical role, helping organizations secure remote work environments without sacrificing productivity or scalability.
The Challenge: Securing a Distributed Workforce
Remote work environments introduce complexity across people, processes, and technology.
Common security challenges include:
- Increased phishing and social engineering attacks
- Insecure home networks and unmanaged devices
- Limited visibility into user behavior and access patterns
- Compliance gaps across jurisdictions and data locations
According to ENISA, remote work has become a primary driver of new enterprise cyber risk exposure in Europe. https://www.enisa.europa.eu
The Expert Approach: Risk-Based Remote Security Design
Cyber security experts focus on risk prioritization, not blanket controls.
Their approach typically includes:
- Identifying critical assets and access paths
- Mapping user roles and privilege levels
- Applying proportional controls based on data sensitivity
- Aligning security measures with business workflows
This ensures that security strengthens the environment rather than slowing teams down.
Endpoint Security and Device Management
Securing the First Line of Defense
Endpoints are the most targeted entry point in remote environments.
Cyber security experts implement:
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
- Device posture checks before access is granted
- Centralized patching and vulnerability management
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
NIST highlights endpoint visibility and continuous monitoring as core requirements for remote access security. https://www.nist.gov
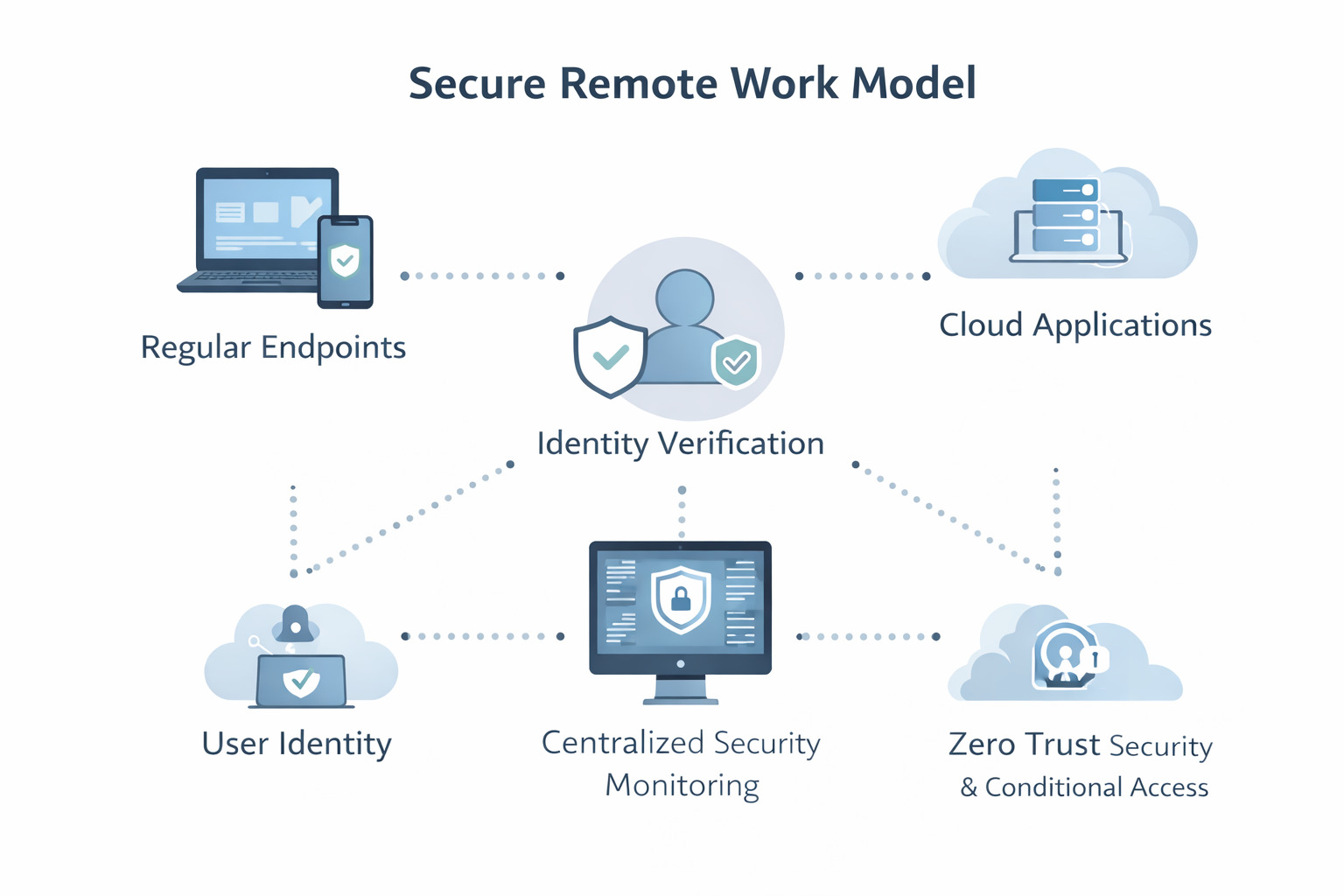
Zero Trust and Secure Access Models
Moving Beyond the Corporate Perimeter
Modern remote work relies heavily on Zero Trust security principles.
Key elements include:
- Identity-first authentication and authorization
- Least-privilege access enforcement
- Continuous verification of users and devices
- Network segmentation and micro-perimeters
Zero Trust ensures that access decisions are dynamic, reducing the impact of compromised credentials.
The Technology Factor: Cloud and Collaboration Security
Remote teams depend on cloud-based tools for daily operations.
Cyber security experts focus on:
- Securing SaaS platforms and cloud workloads
- Implementing conditional access policies
- Monitoring data movement across applications
- Preventing shadow IT and unsanctioned integrations
ISO/IEC 27001 emphasizes access control and monitoring as essential for distributed work models. https://www.iso.org
Industry Insight
Gartner reports that organizations with mature remote security strategies reduce successful cyber incidents by over 40 percent compared to those relying on legacy perimeter defenses.
Additionally, McKinsey notes that secure remote work capabilities are now a key factor in employee retention and operational continuity. https://www.mckinsey.com
These insights highlight cyber security as both a risk management and business enablement function.
Euro IT Sourcing Perspective
From our experience working with European technology-focused companies, remote work security is most effective when cyber security experts are involved early in workforce and infrastructure planning.
We observe stronger outcomes when organizations:
- Integrate security into remote onboarding processes
- Align cyber security teams with HR and IT operations
- Treat remote security as an ongoing program, not a one-time setup
This approach supports scalability while meeting European compliance and data protection expectations.
Results and Business Impact
Organizations that engage cyber security experts for remote environments typically achieve:
- Reduced incident response times
- Improved compliance with GDPR and internal policies
- Higher employee trust in digital systems
- Lower operational disruption from security events
Industry benchmarks suggest mature remote security programs can reduce breach-related costs by up to 25 percent annually.
Key Takeaways
- Remote work significantly expands the cyber attack surface
- Cyber security experts apply risk-based, business-aligned controls
- Endpoint and identity security are foundational
- Zero Trust models strengthen access governance
- Secure remote work enables long-term resilience and growth
Author and Contact
Author: Matt Borekci
Contact Us: Euro IT Sourcing

What Does a Cyber Security Expert Do? A Complete Guide
Discover what a cyber security expert does, their roles, skills, and how they protect businesses from digital threats.

How Much Does a Cyber Security Expert Earn? Salary Insights for 2025
Explore 2025 cybersecurity salary trends, including global averages, roles in demand, and how outsourcing impacts IT security hiring.